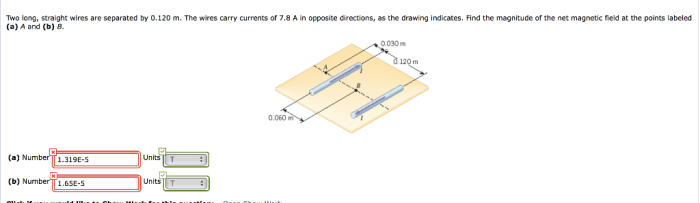
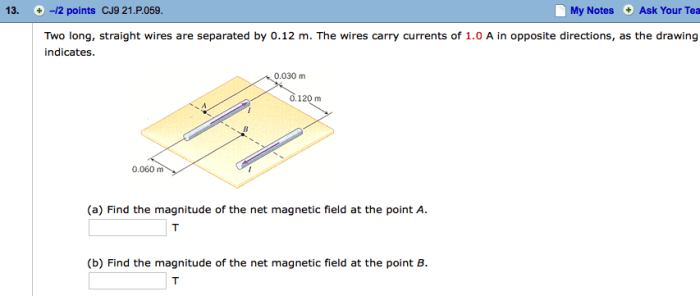
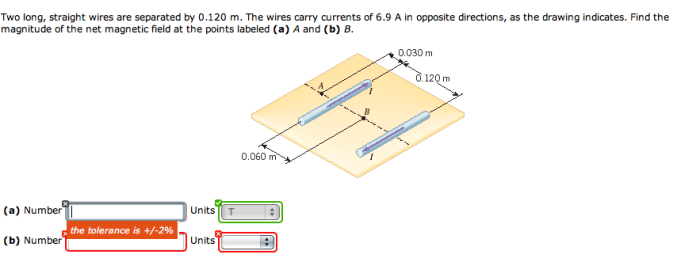
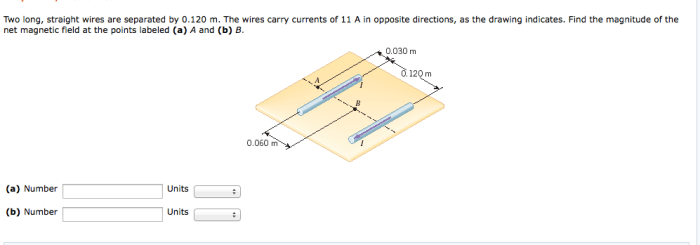
Two long straight wires are separated by 0.120 m – Two long straight wires separated by 0.120 m carry currents in the same direction. The magnetic force between the wires is a fundamental concept in electromagnetism with practical applications in various electrical devices. This article delves into the underlying principles, calculations, and applications of this magnetic interaction.
The magnetic field created by each wire interacts with the other, resulting in a magnetic force. Understanding the relationship between current, distance, and magnetic force is crucial for designing and analyzing electrical systems.
Basic Concepts: Two Long Straight Wires Are Separated By 0.120 M
Electric fields arise from electric charges, while magnetic fields arise from electric currents. Electric fields exert forces on charges, while magnetic fields exert forces on moving charges or current-carrying wires. The interaction between electric and magnetic fields is a fundamental aspect of electromagnetism.
Magnetic Field of a Current-Carrying Wire
The Biot-Savart law describes the magnetic field around a current-carrying wire. For a long straight wire, the magnetic field lines form concentric circles around the wire. The magnetic field strength decreases inversely with the distance from the wire.
Interaction of Two Parallel Wires
Two parallel current-carrying wires experience a magnetic force between them. The direction of the force depends on the direction of the currents. The force per unit length between the wires is given by the expression F = μ0I1I2/(2πd), where μ0 is the permeability of free space, I1 and I2 are the currents in the wires, and d is the distance between them.
Applications
The interaction between parallel wires is utilized in electromagnets and transformers. Electromagnets use coils of wire to generate magnetic fields, while transformers use the magnetic field between coils to transfer electrical energy.
Magnetic Field Visualization, Two long straight wires are separated by 0.120 m
The magnetic field lines around two parallel wires can be visualized using a table or diagram. The lines form concentric circles around each wire, and the direction of the field is indicated by the direction of the lines.
FAQ Guide
What is the direction of the magnetic force between two parallel wires carrying currents in the same direction?
The magnetic force is attractive, causing the wires to move towards each other.
How does the magnetic force change if the distance between the wires is doubled?
The magnetic force decreases to one-fourth of its original value.
What practical applications utilize the magnetic force between parallel wires?
Electromagnets, transformers, and motors are examples of devices that harness this force.