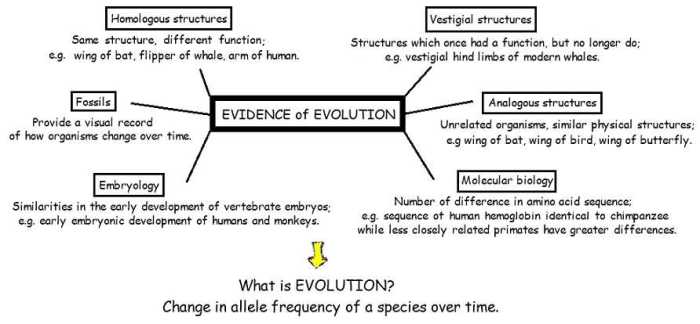
Chapter 10 Principles of Evolution Answer Key unveils the profound concepts that govern the intricate tapestry of life’s evolution. This comprehensive guide delves into the fundamental principles that shape the diversity and adaptation of species, providing a roadmap to understanding the mechanisms that drive the ever-changing panorama of life on Earth.
Through a captivating exploration of natural selection, genetic variation, population genetics, speciation, phylogenetics, molecular evolution, and human evolution, this answer key illuminates the complex processes that have shaped the history of life and continue to influence its trajectory.
1. Natural Selection

Natural selection is a fundamental mechanism of evolution that explains how populations of organisms adapt to their environments over generations. It was first proposed by Charles Darwin in his groundbreaking work, “On the Origin of Species.” Natural selection operates through the following key principles:
- Variation:Individuals within a population exhibit variation in their traits, which can be inherited from their parents.
- Overproduction:Populations tend to produce more offspring than can survive and reproduce.
- Competition:Individuals compete for limited resources, such as food, mates, and shelter.
- Differential Survival and Reproduction:Individuals with traits that make them better adapted to their environment have a higher chance of surviving and reproducing.
- Inheritance:The advantageous traits are passed on to offspring through inheritance.
Over time, natural selection leads to the accumulation of favorable traits in a population, resulting in adaptation to the specific environmental conditions. This process can drive significant evolutionary changes, shaping the diversity and complexity of life on Earth.
Examples of Natural Selection
- Peppered Moths:In industrial areas during the Industrial Revolution, dark-colored peppered moths had an advantage over light-colored ones, as they were better camouflaged against the soot-covered trees. This led to a shift in the population towards darker moths.
- Antibiotic Resistance:When bacteria are exposed to antibiotics, some individuals may have genetic variations that confer resistance. These individuals survive and reproduce, passing on their resistant genes to their offspring. Over time, the population becomes increasingly resistant to the antibiotic.
Role of Environmental Pressures, Chapter 10 principles of evolution answer key
Environmental pressures, such as climate change, habitat loss, and predation, play a crucial role in driving natural selection. These pressures create selective forces that favor individuals with traits that enhance their survival and reproductive success in the specific environment.
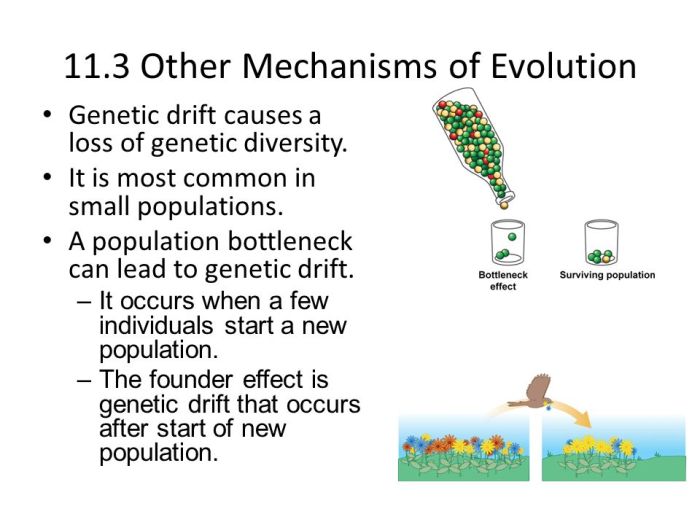
2. Genetic Variation
Genetic variation is the presence of differences in DNA sequences among individuals within a population. It is the raw material upon which natural selection acts, providing the necessary variation for adaptation and evolution.
- Importance:Genetic variation allows populations to adapt to changing environmental conditions, increases resilience to diseases, and promotes the evolution of new species.
- Sources:Genetic variation arises from various sources, including mutations (random changes in DNA), genetic recombination during meiosis, and gene flow between populations.
Contributions to Trait Diversity
Genetic variation contributes to the diversity of traits within a population, which is essential for adaptation and survival. Individuals with different genetic variations may exhibit different phenotypes, such as size, color, behavior, and resistance to diseases. This variation allows populations to occupy diverse ecological niches and exploit a wide range of resources.
FAQ Explained: Chapter 10 Principles Of Evolution Answer Key
What is the fundamental concept of natural selection?
Natural selection is the process by which individuals with traits that enhance their survival and reproductive success in a given environment are more likely to pass on those traits to their offspring.
How does genetic variation contribute to evolution?
Genetic variation provides the raw material for evolution by introducing new traits and characteristics into a population, increasing its adaptability to changing environmental conditions.
What is the significance of population genetics in evolutionary studies?
Population genetics provides a framework for understanding the distribution and transmission of genetic variation within populations, enabling researchers to analyze changes in allele frequencies over time and infer evolutionary processes.
How is speciation defined, and what are its different modes?
Speciation is the process by which new species arise. Different modes of speciation include allopatric speciation (geographic isolation), sympatric speciation (within the same geographic area), and parapatric speciation (along an environmental gradient).
What is the role of molecular evolution in understanding evolutionary relationships?
Molecular evolution analyzes changes in DNA and protein sequences over time, providing insights into the genetic relatedness of species and the evolutionary history of life.